- Feature Paper
- Article
Synergistic Cellular Toxicity from Inhibition of Poly(ADP-ribose) Glycohydrolase (PARG) and Ubiquitin-Specific Protease 1 (USP1)
- Stefan M. Leonard,
- Charlotte R. Pearson and
- Robert W. Sobol
- + 1 author
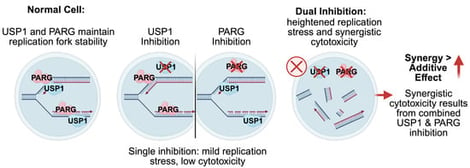
Ubiquitin-specific protease 1 (USP1) is an emerging target for poly(ADP-ribose) polymerase 1 (PARP1) inhibitor-resistant and BRCA1/BRCA2 mutant tumors. USP1 is a deubiquitylating enzyme responsible for the removal of the mono-ubiquitin mark on FANCD2, PARP1, and the replication factor proliferating cell nuclear antigen (PCNA), among other proteins. USP1 facilitates proper PCNA-mediated polymerase switching from error-prone trans-lesion synthesis DNA polymerases to replicative DNA polymerases. Due to the critical role of USP1 in DNA synthesis and DNA repair, and the discovery that USP1 deubiquitylates PARP1, USP1 inhibitors (USP1i) were found to have a synthetic lethal relationship with PARP1 inhibitors (PARPi), suggesting a mechanistic link between poly(ADP-ribose) (PAR) dynamics and USP1-mediated ubiquitin hydrolysis. However, the relationship between USP1 inhibition and inhibitors of poly(ADP-ribose) glycohydrolase (PARGi), the primary enzyme responsible for PAR hydrolysis, has not been resolved. Using cell cytotoxicity, synergy, PCNA-ubiquitin, and PAR analyses, it is demonstrated herein that PARG inhibition, combined with USP1 inhibition, leads to increased levels of mono-ubiquitinated PCNA, decreased PAR accumulation, and synergistic cytotoxicity between ML323, a potent USP1i, and PDD00017273, a model PARGi. Future studies will focus on the mechanism that contributes to USP1/PARG synthetic lethality, the mechanism of cell death, and the impact of USP1 on PAR/ubiquitin dynamics and replication stress signaling.
10 February 2026